6 Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
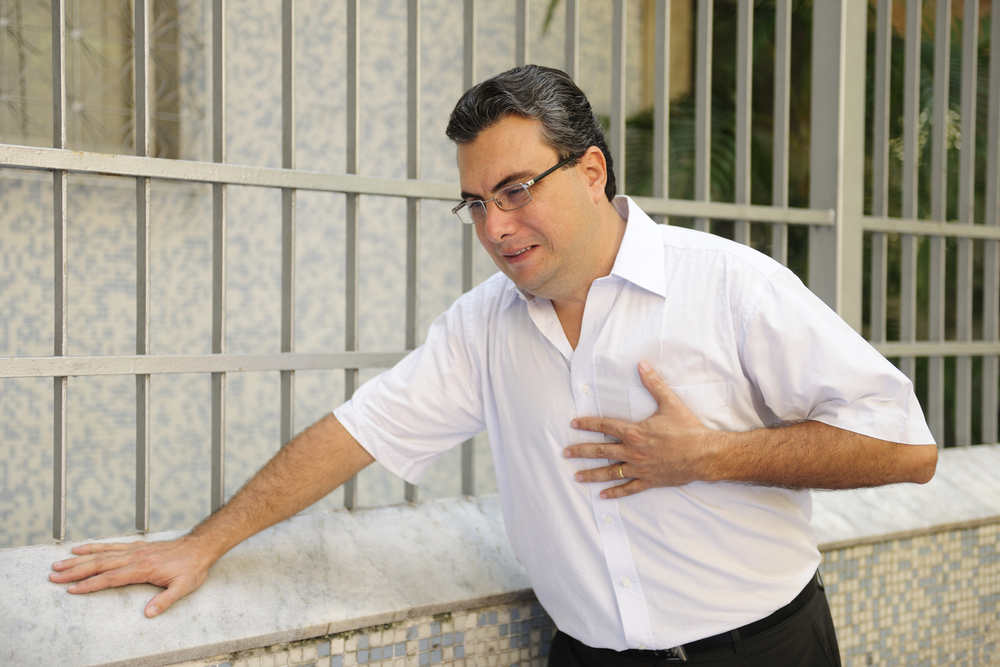
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and rapid heart rhythm, where the heart pulses differently than it’s typical rate. This abnormal rhythm is the result of different impulses firing at once. For most people, atrial fibrillation usually has no symptoms. However, it may cause shortness of breath, general weakness, or a pounding heartbeat.
Below are six common causes of atrial fibrillation:
1. Congenital heart defects or heart valve issues
A congenital heart defect (CHD) is an abnormality in the structure of the heart, usually present from birth. A child may inherit it from a parent, or develop a CHD if their mother is exposed to infection or toxic substances during pregnancy. People with CHD are susceptible to atrial fibrillation due to residual shunts, hypertension, and abnormal vessel anatomy. Individuals with complex to moderate CHD should consider anticoagulation or thromboprophylaxis.
2. Certain lung diseases
Lung diseases like COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) often cause fibrillation. The main symptoms of COPD are shortness of breath and a sputum-producing cough. These diseases usually come with ventricle problems, which lead to atrial fibrillation. The best way to prevent most lung diseases is to avoid tobacco smoke, air pollution, and exposure to fumes, dust, and vapors.
3. Uncontrolled high blood pressure
Hypertension increases the chances of atrial fibrillation, and it happens in many people. The leading causes of uncontrolled high blood pressure are hormone activity, increased levels of stress, and inactivity. To prevent higher blood pressure, individuals should maintain a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and take medication (vasodilators and calcium-channel blockers) if applicable.
4. Heart attack
Heart attacks are another cause of atrial fibrillation, and occur when cholesterol builds up inside the arteries supplying blood to the heart muscles. Arteries shut down when blood clots form due to pieces of plaque breaking free. These defective arteries weaken atrial tissue, resulting in atrial fibrillation. People can avoid this condition by maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
5. Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea involves repeated episodes of breathing issues during sleep. A person might experience their breathing stopping and starting at random while they are sleeping. This condition results in negative swings in the intrathoracic pressure. In particular, sleep apnea often increases the left atrial volume, causing atrial fibrillation. According to multiple studies, you can eliminate apnea through CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) treatment.
6. Thyroid disease
Thyroid disease is another leading cause of atrial fibrillation, since the thyroid hormone directly affects the heart. Thyroid disease raises the heart rate and leads to abnormal heart palpitations and rhythms. These abnormal heart rhythms increase the chance of atrial fibrillation. Symptoms of this condition include sudden weight loss, anxiety, faster heartbeat, and weak muscles. To treat thyroid disease, doctors will commonly prescribe medication to reduce thyroid hormone production. These drugs help reduce overactive thyroid hormones, but are not long-term solutions because their continued use may lead to liver damage. The next step is often thyroid ablation treatment, or in severe cases, thyroid removal, to help prevent atrial fibrillation.