4 Causes of Excess Sweating
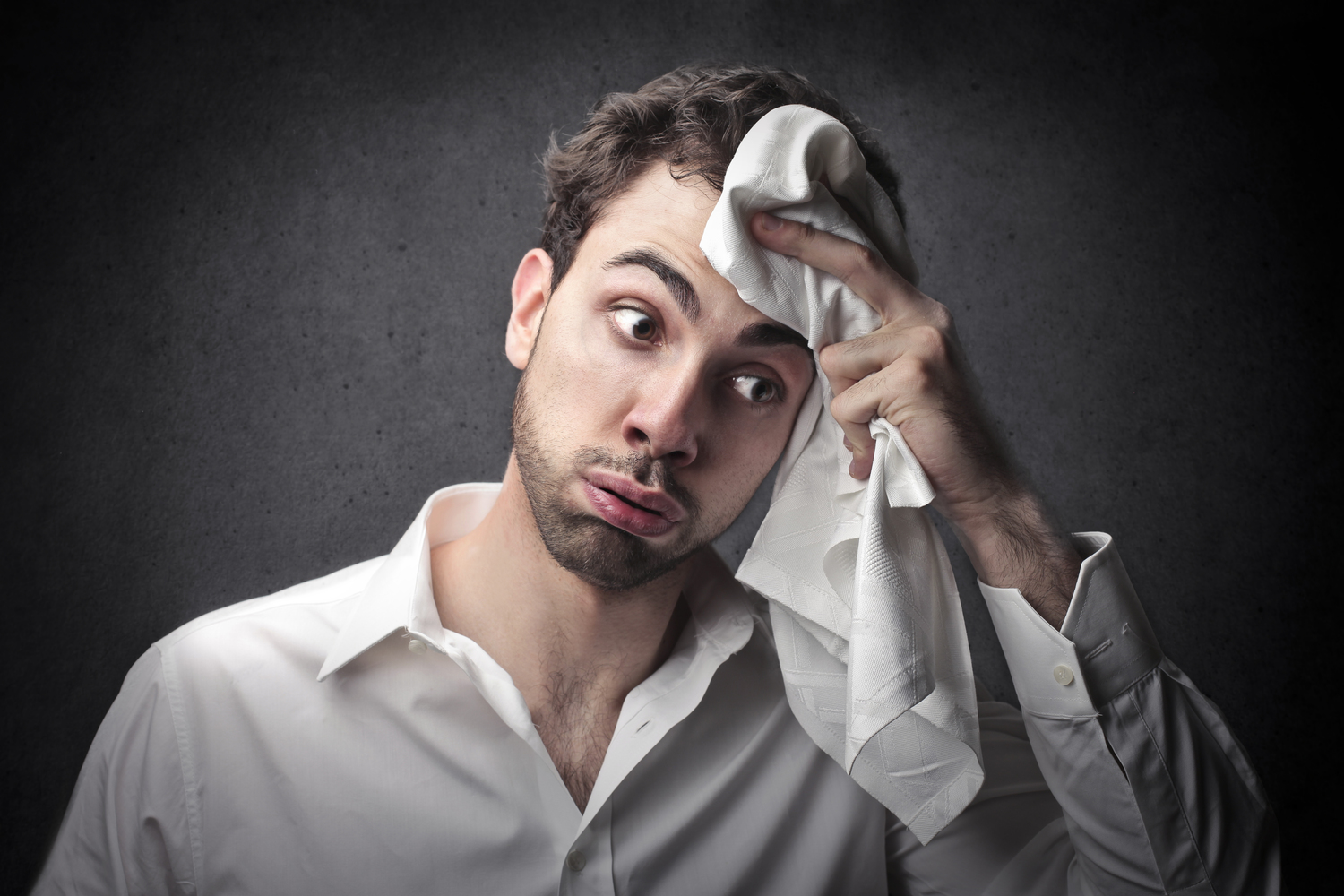
Hyperhidrosis is also referred to as polyhidrosis or seborrhea. This is usually a condition considered as extreme sweating. Typically, the sweating may affect a single place or the entire body. Despite it being the least serious disease it makes the patient feel uncomfortable. The disease usually commences during adolescence.
Symptoms of hyperhidrosis or heavy sweating are clammy or wet palms and soles of the feet, frequent sweating, irritating skin, and psychological trauma leading to depression. Common triggers for heaving sweating include:
1. Hyperthyroidism or overactive thyroid
A condition that makes your thyroid gland to produce too much hormone known as thyroxine. The thyroid usually regulates the heartbeat as well as how fast your calories burn. This condition can increase your metabolism as well as heat sensitivity. Besides the condition speeds up the rate of chemical reactions in the body leading to heavy sweating. Typically, the symptoms differ extensively and more noticeable in the later phases of the illness. Some of the additional signs of hyperthyroidism are, nervousness, mood swings, tiredness or weakness, swollen thyroid or goiter, abrupt loss of weight, uneven heartbeat, thinning skin, tremor, and so on.
2. Heart disease
Happens when blood is blocked hence resisting the flow to the heart. Typically, the blockage is the accumulation of fats or cholesterol that form infection in the coronary artery. This may lead to symptoms of hyperhidrosis or heavy sweating. Some of the symptoms of heart disease are high blood pressure, aching sensation, indigestion, heartburn, abdominal and chest pains, shortness of breath, cold sweat, tiredness, and abrupt dizziness. Also, sweating at night is another heart-based illness known as subacute endocarditis. It is an infection of the heart membrane as well as heart valves. Usually develop gradually than the actual form of the condition. This chest pain, heart attack, and subacute endocarditis are known as secondary hyperhidrosis.
3. Parkinson’s disease
This disease affects the nerve cells found in the brain and that secretes dopamine. Thus it is an advanced nervous system illness that affects movement. This results in the loss of neurons that excrete a chemical messenger in the brain. This leads to sudden blood pressure changes that may trigger excessive sweating. Usually, signs commence slowly with a hardly visible tremor in one hand only. Parkinson’s disease symptoms are tremors or shaking of hands or fingers, limb, legs or the entire body, bradykinesia or slowed movement that makes some tasks complicated as well as time-consuming, muscle rigidity in body parts and which are painful limiting your movement, weakened posture, and stability, loss of involuntary movement or reduced ability to carry out unconscious activities such as smiling,
4. Spinal cord injury
Sweat glands typically develop their innervation from the sympathetic nervous system. Since it does not follow a distinct segmental circulation, sympathetic innervation causes normal sweating. Excessive sweating, therefore, is an indication that your spinal cord is injured. This is normally an indication of mass reflex calamity. Acute spinal cord damage is estimated to lead to a loss of sweating beneath the site of damage. But in some cases, these conditions may be realized after months or years. Patients with spinal cord damage perspire a lot on the face and higher part of the chest.